Oracle Unveils MySQL 8.2 with Enhanced Read/Write Splitting Capabilities
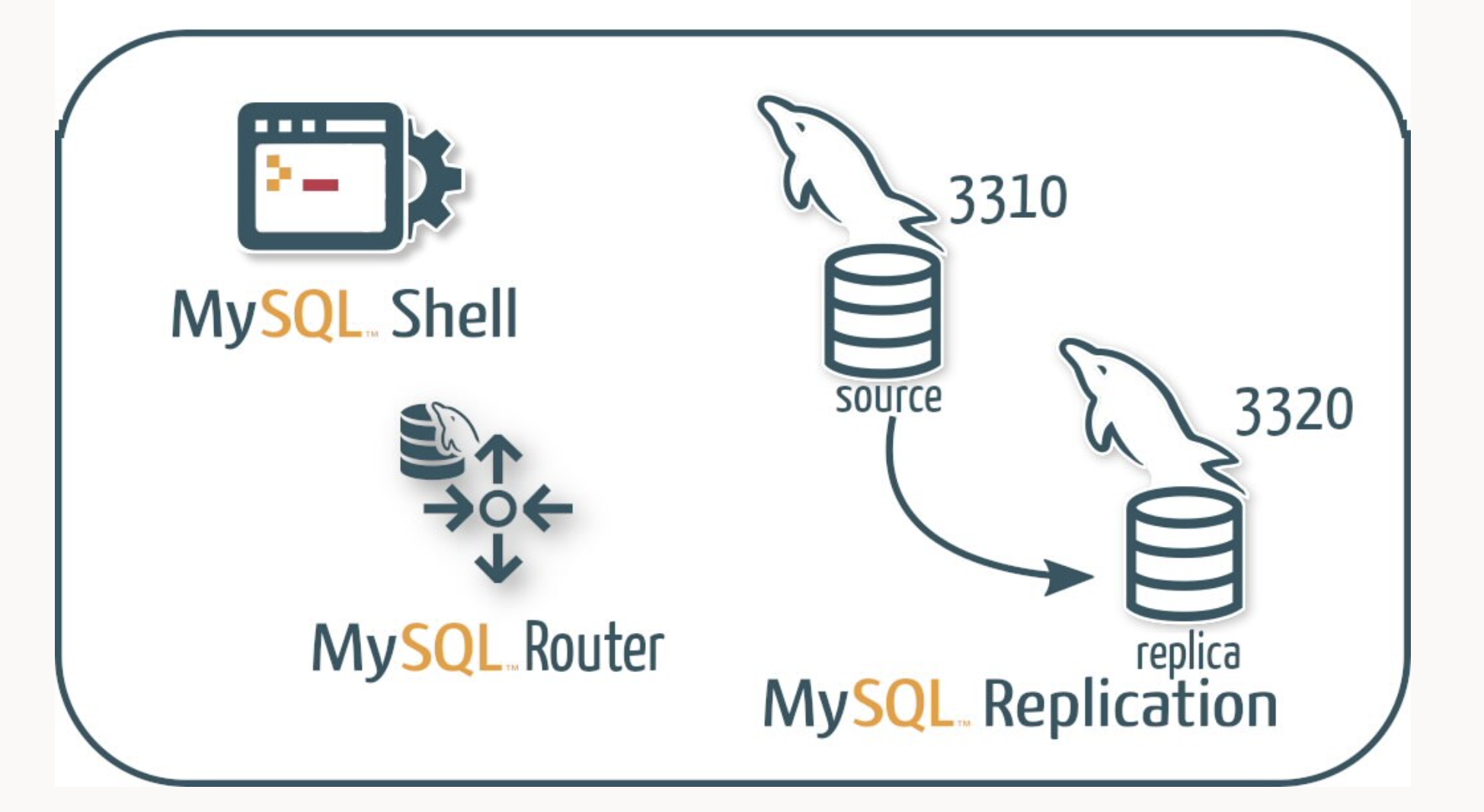
In a recent announcement, Oracle unveiled the general availability of MySQL 8.2, marking a significant milestone in the evolution of this popular relational database management system. One of the standout features introduced in this release is Read/Write Splitting, a long-awaited functionality designed to optimize database performance and scalability.
Read/Write Splitting enables applications to seamlessly direct write traffic to read-write instances while read traffic is directed to read-only instances. The team emphasized the importance of this feature in distributing reads and writes efficiently. They explained that at scale, distributing reads between replicas requires careful management in the application, necessitating the pointing of writes to one destination and reads to another. With MySQL 8.2, MySQL Router now possesses the capability to identify reads and writes, directing them to primary instances in the case of an InnoDB Cluster or to an asynchronous replication source for writes and to secondary instances or replicas for reads.
This newfound capability allows each client session to communicate with both read_write and read_only destinations. The router intelligently classifies each query as a read or write, ensuring it reaches the appropriate backend. However, questions about consistency levels in reads have surfaced.
When connecting to MySQL using the Read/Write Port (defaulting to 6450), connections will reach the replica (secondary) for reads and the replication source (primary) for transactions. This distinction offers flexibility in managing database traffic based on the nature of the operation.
While the community has generally welcomed this feature, some people have raised concerns about the router’s ability to match the timeline consistency provided by MySQL Group Replication. They suggest that tracking consistency across replicas is achievable but requires either a round trip via polling or some form of event notification from the cluster to the router.
Despite these considerations, the team emphasizes the value of this feature in optimizing database performance and scalability without necessitating changes to the application. The seamless integration of Read/Write Splitting enhances the overall user experience and simplifies database management and deployment.
Earlier this year, Oracle introduced a new versioning model for MySQL, featuring innovation and Long-Term Support (LTS) releases. MySQL 8.2.0, the latest quarterly innovation release, has bug fixes, security patches, and new features. These include hash table optimization for set operations, enhancements for MySQL Enterprise Firewall, and the addition of a new WebAuthn authentication method supporting devices such as smart cards, security keys, and biometric readers.
MySQL 8.2.0 is now available for download from the Oracle website, providing users with a powerful toolset for improving their database infrastructure’s performance and scalability. As the MySQL ecosystem continues to evolve, the introduction of Read/Write Splitting in MySQL 8.2 is a pivotal development, addressing key concerns in distributed database management.
Niharika is a Technical consulting intern at Marktechpost. She is a third year undergraduate, currently pursuing her B.Tech from Indian Institute of Technology(IIT), Kharagpur. She is a highly enthusiastic individual with a keen interest in Machine learning, Data science and AI and an avid reader of the latest developments in these fields.