Robbyant Open Sources LingBot World: a Real Time World Model for Interactive Simulation and Embodied AI

Robbyant, the embodied AI unit inside Ant Group, has open sourced LingBot-World, a large scale world model that turns video generation into an interactive simulator for embodied agents, autonomous driving and games. The system is designed to render controllable environments with high visual fidelity, strong dynamics and long temporal horizons, while staying responsive enough for real time control.
From text to video to text to world
Most text to video models generate short clips that look realistic but behave like passive movies. They do not model how actions change the environment over time. LingBot-World is built instead as an action conditioned world model. It learns the transition dynamics of a virtual world, so that keyboard and mouse inputs, together with camera motion, drive the evolution of future frames.
Formally, the model learns the conditional distribution of future video tokens, given past frames, language prompts and discrete actions. At training time, it predicts sequences up to about 60 seconds. At inference time, it can autoregressively roll out coherent video streams that extend to around 10 minutes, while keeping scene structure stable.
Data engine, from web video to interactive trajectories
A core design in LingBot-World is a unified data engine. It provides rich, aligned supervision for how actions change the world while covering diverse real scenes.
The data acquisition pipeline combines 3 sources:
- Large scale web videos of humans, animals and vehicles, from both first person and third person views
- Game data, where RGB frames are strictly paired with user controls such as W, A, S, D and camera parameters
- Synthetic trajectories rendered in Unreal Engine, where clean frames, camera intrinsics and extrinsics and object layouts are all known
After collection, a profiling stage standardizes this heterogeneous corpus. It filters for resolution and duration, segments videos into clips and estimates missing camera parameters using geometry and pose models. A vision language model scores clips for quality, motion magnitude and view type, then selects a curated subset.
On top of this, a hierarchical captioning module builds 3 levels of text supervision:
- Narrative captions for whole trajectories, including camera motion
- Scene static captions that describe environment layout without motion
- Dense temporal captions for short time windows that focus on local dynamics
This separation lets the model disentangle static structure from motion patterns, which is important for long horizon consistency.
Architecture, MoE video backbone and action conditioning
LingBot-World starts from Wan2.2, a 14B parameter image to video diffusion transformer. This backbone already captures strong open domain video priors. Robbyant team extends it into a mixture of experts DiT, with 2 experts. Each expert has about 14B parameters, so the total parameter count is 28B, but only 1 expert is active at each denoising step. This keeps inference cost similar to a dense 14B model while expanding capacity.
A curriculum extends training sequences from 5 seconds to 60 seconds. The schedule increases the proportion of high noise timesteps, which stabilizes global layouts over long contexts and reduces mode collapse for long rollouts.
To make the model interactive, actions are injected directly into the transformer blocks. Camera rotations are encoded with Plücker embeddings. Keyboard actions are represented as multi hot vectors over keys such as W, A, S, D. These encodings are fused and passed through adaptive layer normalization modules, which modulate hidden states in the DiT. Only the action adapter layers are fine tuned, the main video backbone stays frozen, so the model retains visual quality from pre training while learning action responsiveness from a smaller interactive dataset.
Training uses both image to video and video to video continuation tasks. Given a single image, the model can synthesize future frames. Given a partial clip, it can extend the sequence. This results in an internal transition function that can start from arbitrary time points.
LingBot World Fast, distillation for real time use
The mid-trained model, LingBot-World Base, still relies on multi step diffusion and full temporal attention, which are expensive for real time interaction. Robbyant team introduces LingBot-World-Fast as an accelerated variant.
The fast model is initialized from the high noise expert and replaces full temporal attention with block causal attention. Inside each temporal block, attention is bidirectional. Across blocks, it is causal. This design supports key value caching, so the model can stream frames autoregressively with lower cost.
Distillation uses a diffusion forcing strategy. The student is trained on a small set of target timesteps, including timestep 0, so it sees both noisy and clean latents. Distribution Matching Distillation is combined with an adversarial discriminator head. The adversarial loss updates only the discriminator. The student network is updated with the distillation loss, which stabilizes training while preserving action following and temporal coherence.
In experiments, LingBot World Fast reaches 16 frames per second when processing 480p videos on a system with 1 GPU node, and, maintains end to end interaction latency under 1 second for real time control.
Emergent memory and long horizon behavior
One of the most interesting properties of LingBot-World is emergent memory. The model maintains global consistency without explicit 3D representations such as Gaussian splatting. When the camera moves away from a landmark such as Stonehenge and returns after about 60 seconds, the structure reappears with consistent geometry. When a car leaves the frame and later reenters, it appears at a physically plausible location, not frozen or reset.
The model can also sustain ultra long sequences. The research team shows coherent video generation that extends up to 10 minutes, with stable layout and narrative structure.]
VBench results and comparison to other world models
For quantitative evaluation, the research team used VBench on a curated set of 100 generated videos, each longer than 30 seconds. LingBot-World is compared to 2 recent world models, Yume-1.5 and HY-World-1.5.
On VBench, LingBot World reports:
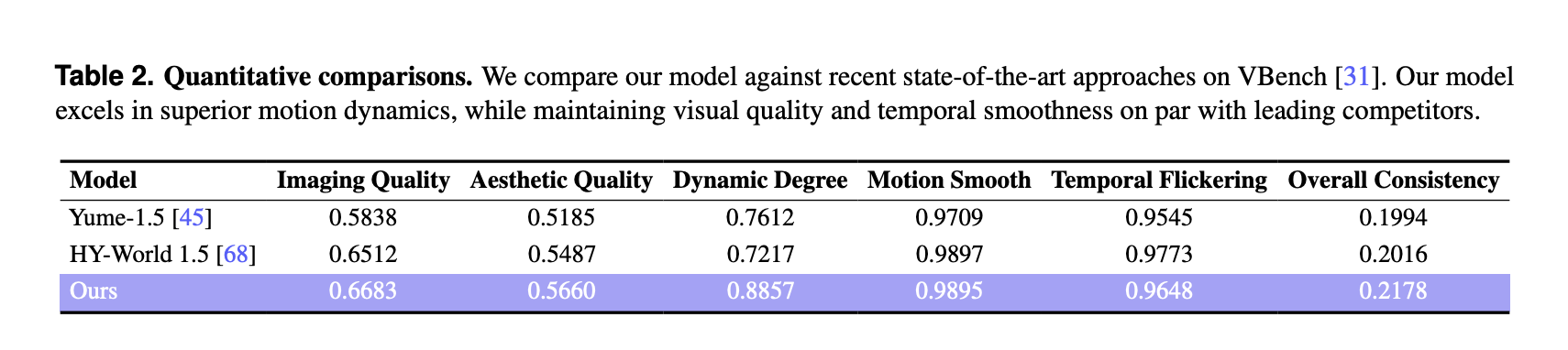
These scores are higher than both baselines for imaging quality, aesthetic quality and dynamic degree. The dynamic degree margin is large, 0.8857 compared to 0.7612 and 0.7217, which indicates richer scene transitions and more complex motion that respond to user inputs. Motion smoothness and temporal flicker are comparable to the best baseline, and the method achieves the best overall consistency metric among the 3 models.
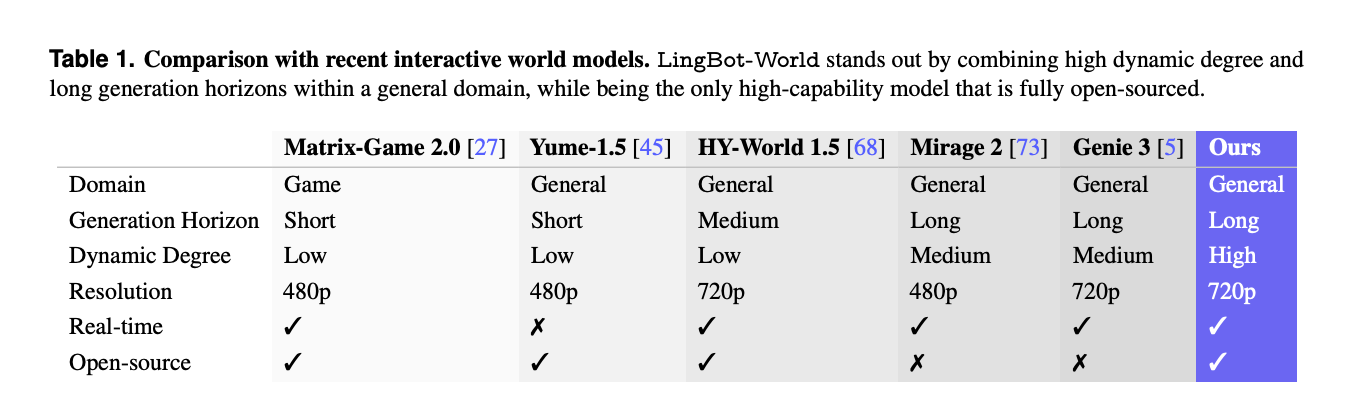
A separate comparison with other interactive systems such as Matrix-Game-2.0, Mirage-2 and Genie-3 highlights that LingBot-World is one of the few fully open sourced world models that combines general domain coverage, long generation horizon, high dynamic degree, 720p resolution and real time capabilities.

Applications, promptable worlds, agents and 3D reconstruction
Beyond video synthesis, LingBot-World is positioned as a testbed for embodied AI. The model supports promptable world events, where text instructions change weather, lighting, style or inject local events such as fireworks or moving animals over time, while preserving spatial structure.
It can also train downstream action agents, for example with a small vision language action model like Qwen3-VL-2B predicting control policies from images. Because the generated video streams are geometrically consistent, they can be used as input to 3D reconstruction pipelines, which produce stable point clouds for indoor, outdoor and synthetic scenes.
Key Takeaways
- LingBot-World is an action conditioned world model that extends text to video into text to world simulation, where keyboard actions and camera motion directly control long horizon video rollouts up to around 10 minutes.
- The system is trained on a unified data engine that combines web videos, game logs with action labels and Unreal Engine trajectories, plus hierarchical narrative, static scene and dense temporal captions to separate layout from motion.
- The core backbone is a 28B parameter mixture of experts diffusion transformer, built from Wan2.2, with 2 experts of 14B each, and action adapters that are fine tuned while the visual backbone remains frozen.
- LingBot-World-Fast is a distilled variant that uses block causal attention, diffusion forcing and distribution matching distillation to achieve about 16 frames per second at 480p on 1 GPU node, with reported end to end latency under 1 second for interactive use.
- On VBench with 100 generated videos longer than 30 seconds, LingBot-World reports the highest imaging quality, aesthetic quality and dynamic degree among Yume-1.5 and HY-World-1.5, and the model shows emergent memory and stable long range structure suitable for embodied agents and 3D reconstruction.
Check out the Paper, Repo, Project page and Model Weights. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 100k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter. Wait! are you on telegram? now you can join us on telegram as well.
The post Robbyant Open Sources LingBot World: a Real Time World Model for Interactive Simulation and Embodied AI appeared first on Tokention.